Kidney Transplant in Indore
Restoring Function and Freedom: Kidney Transplant Expertise at Jupiter Hospital
Our bodies house two kidney organs, resembling beans, strategically positioned on either side of the vertebral column beneath the diaphragm in the upper part of the abdomen. These crucial organs play a pivotal role in sustaining overall health by eliminating waste products, excess water, and salt, while also regulating blood pressure, bone health, and hemoglobin levels. When these functions are compromised, kidney failure emerges as a life-threatening concern, presenting in two forms: acute (temporary) and chronic (permanent). Chronic kidney failure, also termed end-stage kidney failure, signifies irreversible damage to the kidneys.
For those in search of Kidney Transplant treatment in Indore, solace awaits in advanced medical facilities. As kidney function reaches the end stage, demanding a permanent solution, a kidney transplant emerges as a critical option. Our Kidney Transplant hospital in Indore promises a better quality of life, extended survival, and fewer dietary restrictions.
Looking for the Kidney Transplant in Indore
Causes of End-stage kidney failure (Permanent irreversible damage to the kidney)
Common causes include:
- Persistently uncontrolled blood sugar from diabetes can damage kidneys, making it the most common cause of end-stage kidney failure.
- Chronic glomerulonephritis, characterized by inflammation of the filter due to altered immune system, presents with proteins in the urine, high blood pressure, and increased creatinine.
- Chronic uncontrolled high blood pressure.
- Chronic recurrent kidney infections known as chronic pyelonephritis.
- Chronic obstruction to urine flow by stones, prostate, cervical cancers (in females).
- Hereditary or familial diseases like multiple cysts in the kidney, single kidney, and developmental abnormalities of the urinary bladder can also damage kidneys.
Treatment options for patients suffering from end-stage kidney disease include:

Hemodialysis
This artificial kidney performs excretory functions, removing waste products, excess salt, water, potassium, and phosphorus. Blood is pumped through a dialyzer filter (artificial kidney) by a machine and then returned to the body. This treatment can be done at a center or at home.

Peritoneal dialysis
The peritoneal membrane in the abdomen acts as a filtering membrane and fluid is pumped into the abdomen via a catheter, exchanged every 4-6 hours daily. It’s a home-based therapy that includes slow dialysis with no stress on the heart or blood pressure fluctuations.
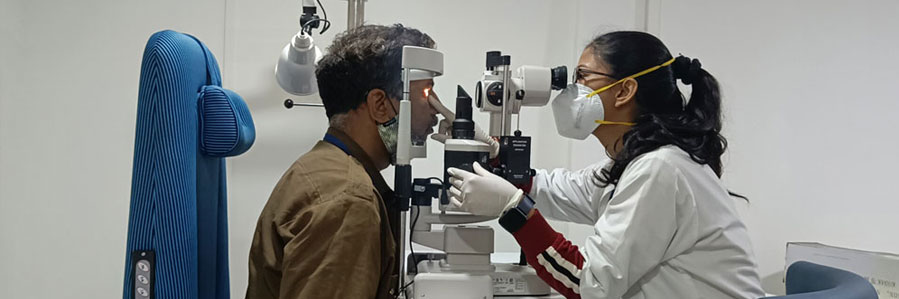
Kidney transplant
It is the treatment of choice for end-stage kidney disease. In the process, one healthy kidney from a living donor (family member or unrelated with no commercial deal) or a brain-dead donor is surgically inserted into the recipient. The transplanted kidney performs all functions required to make up for a failed kidney.

Living Donor Transplant
The kidney is donated usually from a family member like father, mother, or siblings preferably. If a related donor is not available, an unrelated donor may be considered. However, the kidney donation cannot entail any commercial deal between the donor and recipient.
Braindead Donor Transplant
If a living donor is not available, individuals can register through a hospital with a zonal coordination center for a deceased donor transplant, also known as a Brain-dead or cadaver transplant. The transplant occurs when a suitable kidney becomes available. However, the primary challenge lies in the extended waiting list, often taking 3-5 years to secure a kidney, contingent on the frequency of donations.
While waiting for a transplant
- Remain relatively healthy and free from infection.
- Take regular and adequate dialysis.
- Avoid excessive weight gain between dialysis.
- Do not miss or ignore regular dialysis visits.
- Consume adequate proteins during dialysis.
- Control blood pressure.
- Maintain hemoglobin between 10-12 g/dl.
- Regular monthly health check-ups and blood tests.
- Engage in regular exercise, avoid smoking and alcohol consumption.
- Take all medications regularly.
- Undergo regular heart check-ups while on dialysis.

Do You Have Any Query
Please fill out the form & our representative will contact you within 24hrs.








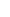






 View Map
View Map

 Book an Appointment
Book an Appointment Find a Doctor
Find a Doctor Health Check-up
Health Check-up



 Find a Doctor
Find a Doctor Health Checkup
Health Checkup Book an Appointment
Book an Appointment