Haematology and BMT in Dombivli
Advanced Haematology and BMT Services with Individualised Care Approaches
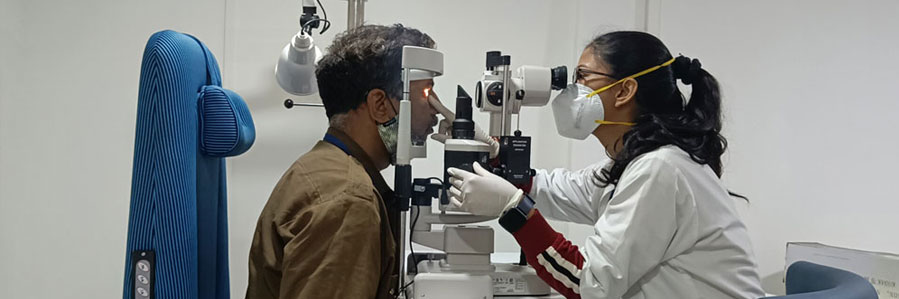
The haematology and bone marrow transplant (BMT) department at Jupiter Hospital functions as a specialised centre for the evaluation and management of complex blood and bone marrow disorders. Recognised as a haematology best hospital in Dombivli, the department provides structured care for patients requiring advanced haematology services and transplant-based treatment.
Services are delivered by an experienced team of haematologists, transplant physicians, and clinical specialists who manage both benign and malignant blood disorders. Patients seeking haematology and BMT treatment in Dombivli benefit from coordinated care pathways designed to support diagnosis, treatment planning, transplantation, and long-term follow-up.
A multidisciplinary model guides treatment decisions, particularly in conditions such as leukaemia, lymphoma, myeloma, and marrow failure syndromes. Individualised treatment protocols are developed for adult and paediatric patients, ensuring continuity of care throughout the transplant journey.
Clinical Infrastructure and Department Capabilities
The Haematology and BMT Centre is supported by specialised infrastructure and trained clinical teams that enable safe and controlled transplant care. The unit integrates inpatient, outpatient, and critical care services under one clinical framework.
Team
Looking for the Haematology and BMT in Dombivli
The Haematology and BMT Centre is supported by specialised infrastructure and trained clinical teams that enable safe and controlled transplant care. The unit integrates inpatient, outpatient, and critical care services under one clinical framework.
Key infrastructure features include:
- Dedicated transplant suites with HEPA filtration
- Isolation rooms for adult and paediatric patients
- 24×7 critical care and monitoring facilities
- Outpatient daycare services for therapy administration
Clinical services available within the department include chemotherapy, immunotherapy, blood transfusion support, endoscopy, bronchoscopy, and dialysis, ensuring comprehensive medical support during treatment.
Transfusion Medicine Services
The transfusion medicine unit provides continuous access to screened and processed blood components required for haematological care and transplant support.
Core services include:
- Platelet apheresis
- NAT-tested blood components
- Peripheral stem cell collection
- Bone marrow processing and preservation
- Gamma irradiation facilities
These services operate round-the-clock to support emergency and planned transplant requirements.
Advanced Diagnostic and Laboratory Support
Accurate diagnosis and disease monitoring are supported through a wide range of laboratory services. These facilities assist in disease classification, treatment response assessment, and transplant readiness evaluation.
Laboratory services include:
- Haematology testing
- Flow cytometry
- Histopathology
- Microbiology
- Drug level assays
Investigations such as peripheral smear analysis, reticulocyte count, and bone marrow aspiration and biopsy are routinely performed to guide clinical decisions.
Blood Disorders and Cancers Managed
The department manages a broad spectrum of haematological conditions, ranging from common disorders to rare and complex diseases.
Conditions treated include:
- Anaemia and clotting dysfunction
- Bone marrow failure syndromes
- Acute and chronic leukaemia
- Multiple myeloma
- Hodgkin’s and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma
- Myeloproliferative and lymphoproliferative disorders
- Neutropenia and leukopenia
Patients seeking acute leukaemia treatment in Dombivli receive care aligned with disease stage and transplant eligibility.
Consultative Haematology and Transplant Services
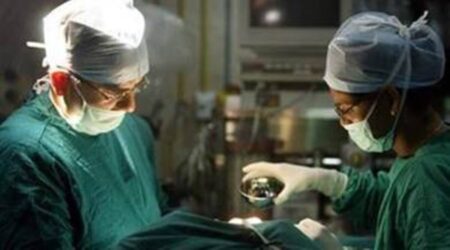
The department offers consultative services for patients requiring transplant-based therapy. Both autologous and allogeneic bone marrow transplants are performed using bone marrow, peripheral blood stem cells, or cord blood stem cells, depending on clinical indication.
These services are utilised for both malignant and non-malignant conditions requiring stem cell replacement.
Bone marrow transplantation is a therapeutic procedure aimed at replacing diseased or dysfunctional marrow with healthy stem cells. These stem cells may be harvested from bone marrow or peripheral blood and are capable of restoring normal blood cell production.
Role of Bone Marrow in Blood Formation
Bone marrow contains primitive stem cells responsible for producing red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. These cells are essential for oxygen transport, immune defence, and clotting function.
Types of Bone Marrow
Bone marrow exists in two forms:
- Red marrow, rich in stem cells and predominant in children
- Yellow marrow, which contains more fat cells and increases with age
In adolescents and adults, red marrow remains concentrated in bones such as the pelvis, sternum, ribs, spine, skull, and the ends of long bones.
Bone Marrow Transplant for Blood Disorders
Bone marrow transplantation is used in both malignant and benign conditions where standard therapies are insufficient.
Malignant Blood Disorders
Malignant haematological conditions involve abnormal growth or function of blood-forming cells and often require a combination of intensive medical therapy and bone marrow transplantation for effective management. These disorders typically affect the bone marrow, lymphatic system, or blood cells and may progress rapidly if not treated in a timely manner.
Conditions managed under this category include:
- Acute and chronic leukaemia (myeloid and lymphoid), where abnormal white blood cells interfere with normal blood production
- Multiple myeloma, a plasma cell disorder affecting bone marrow function
- Myelodysplastic syndromes are marked by ineffective blood cell production
- Hodgkin’s and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, cancers originating in the lymphatic system
- Myeloproliferative disorders involve excessive production of one or more blood cell types
- Selected solid tumours, such as neuroblastoma and Ewing’s sarcoma, where transplantation may be indicated as part of treatment
Benign Haematological Conditions
Certain non-cancerous blood disorders may also require bone marrow or stem cell transplantation due to bone marrow failure, genetic abnormalities, or severe immune dysfunction. These conditions often present early in life and require long-term management.
Disorders treated under this group include:
- Thalassemia major and sickle cell disease
- Aplastic anaemia
- Congenital neutropenia and Leukocyte Adhesion Deficiency (LAD)
- Immunodeficiency disorders
- Bone marrow failure syndromes
- Haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH)
- Inherited metabolic and paediatric syndromes
Types of Bone Marrow Transplant
The choice of bone marrow transplant depends on several factors, including the underlying disease, disease stage, donor availability, and the patient’s overall clinical condition. A detailed medical evaluation helps determine the most appropriate transplant approach.
Autologous Transplant
In an autologous transplant, stem cells are collected from the patient’s own blood or bone marrow and stored safely. After high-dose therapy, these cells are reinfused to restore bone marrow function and support recovery.
Allogeneic Transplant
An allogeneic transplant involves stem cells sourced from a compatible donor. Donor selection is based on human leukocyte antigen (HLA) matching to reduce the risk of complications and improve transplant outcomes.
Variants of Allogeneic Transplants
Allogeneic transplants use stem cells from a donor and are selected based on donor compatibility and patient needs. The main variants include:
- HLA-Matched Related Donor (Sibling) Transplant Stem cells are sourced from a sibling with a complete HLA match, offering better compatibility and reduced risk of complications.
- HLA-Matched Unrelated Donor Transplant When a related donor is unavailable, stem cells are obtained from an unrelated donor with a full HLA match identified through donor registries.
- Haplocordentical Donor Transplant This option uses stem cells from a partially matched donor, usually a parent or sibling, and is considered when no fully matched donor is available.
- Umbilical Cord Blood Transplant Stem cells collected from a newborn’s umbilical cord are used, allowing transplantation with less stringent matching requirements.
After stem cells are collected, they are carefully filtered to remove unwanted components such as fat and debris. The cells are then processed, tested, counted, and prepared in specialised laboratories before being readied for infusion. This controlled preparation ensures safety and accuracy throughout the transplant process at our haematology best hospital in Dombivli.
Personalised Transplant Planning
The type of transplant recommended depends on the patient’s medical condition, diagnosis, and overall health status. A detailed clinical evaluation by a BMT specialist in Dombivli helps determine the most suitable transplant approach. The primary objective of bone marrow transplantation is to manage complex blood disorders and selected cancers through targeted, patient-specific care.
Stages of the Bone Marrow Transplant Process
Bone marrow transplantation is carried out in clearly defined stages, each designed to support treatment effectiveness and patient safety.
Phase 1: Pre-Transplant Assessment
This stage focuses on complete medical evaluation and preparation. It includes diagnostic testing, assessment of organ function, and conditioning to prepare the body for transplant.
Phase 2: Stem Cell Infusion
Stem cells collected from the patient (autologous) or a donor (allogeneic) are infused into the bloodstream. This step marks the actual transplant and is performed under close medical supervision.
Phase 3: Post-Transplant Care
After infusion, patients are closely monitored for recovery and early complications. Medical teams focus on infection prevention, immune management, and supporting stem cell engraftment.
Bone Marrow Transplant Treatment Pathway
Step 1: Initial Preparation
The transplant journey begins with admission to the BMT unit, where evaluations are completed, a multidisciplinary care plan is finalised, and a central venous catheter is placed.
Step 2: Stem Cell Collection
Stem cells are harvested either from bone marrow or peripheral blood. In donor-based transplants, cells are collected from a matched donor; in autologous transplants, cells come from the patient.
Step 3: Conditioning Therapy
Patients receive chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or both to suppress existing bone marrow function. This step improves the effectiveness of the transplant and may be delivered on an inpatient or outpatient basis.
Step 4: Transplant Infusion
Prepared stem cells are infused into the bloodstream, similar to a blood transfusion. This transition marks the start of the recovery phase.
Step 5: Engraftment Monitoring
Patients remain under continuous observation while the new stem cells begin producing healthy blood cells. Supportive care is provided to reduce infection risk.
Step 6: Early Recovery
Within two to three weeks, early signs of engraftment usually appear. Ongoing monitoring continues, and discharge planning begins once stability is achieved.
Step 7: Long-Term Follow-Up
After discharge, patients gradually return to their daily routines with regular follow-ups. Long-term monitoring helps prevent late complications and supports sustained recovery under the guidance of the best bone marrow transplant doctor in Dombivli.
Patients Speak
Hear the heartwarming stories of patients overcoming difficult afflictions












 View Map
View Map Book an Appointment
Book an Appointment Find a Doctor
Find a Doctor Health Check-up
Health Check-up











 Find a Doctor
Find a Doctor Health Checkup
Health Checkup Book an Appointment
Book an Appointment