Haematology and BMT in Pune
Haematology and BMT: Your Comprehensive Center for Blood Disorders and Bone Marrow Transplantation
Jupiter Hospital, located in Pune, stands out as one of India's prime private quaternary care hospitals. The Haematology & Bone Marrow Transplant (BMT) department is a crucial specialty here. Our centre excels in providing specialised Haematology and BMT treatment in Pune, ensuring accessible care for patients grappling with complex blood disorders.
Our team of accomplished transplant specialists is internationally renowned, guided by principles of innovation, collaboration, confidentiality, empathy, and integrity. Over the years, we have amassed a wealth of experience, successfully performing a multitude of transplants for patients from various corners of the world, each dealing with unique blood disorders.
When it comes to addressing cancer and blood diseases like leukaemia, lymphoma, myeloma, and other conditions necessitating transplants, we have a multidisciplinary approach at our Haematology and BMT hospital in Pune. Our commitment extends to formulating individualised treatment plans for all patients, irrespective of age, tailored to address their specific and evolving needs before, during, and after the transplant.
Team
Looking for the Haematology and BMT in Pune
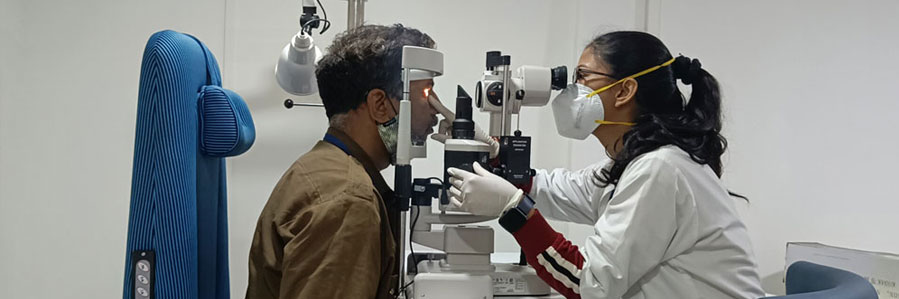
The Centre is equipped with the right infrastructure and a team of highly experienced, internationally trained specialists. It offers transfusion services, laboratories, and a fully-equipped radiation oncology unit.
Comprehensive Key Features
Key features include a unique city-exclusive unit, round-the-clock Advanced Critical Care Services, spacious transplant suites with HEPA filters, Adult and Care Unit with isolation beds, outpatient daycare, and a wide range of medical services, from Chemotherapy and Immunotherapy to Blood Transfusion, Endoscopy, Bronchoscopy, and Dialysis.
Transfusion Medicine Department
The department operates 24/7 and offers a broad range of blood components, including platelet apheresis, NAT-tested blood components, peripheral stem cell harvesting, bone marrow processing, and stem cell preservation through cryopreservation. They also have a Gamma Irradiator.
Diverse Laboratory Services
Laboratory services encompass Haematology, Flow Cytometry, HCA, Microbiology, Drug Assays, and Histopathology.
Treatment for Varied Blood Disorders
The Centre specialises in diagnosing and treating a wide spectrum of blood disorders and blood cancers, addressing anaemia, marrow failure syndromes, coagulation disorders, acute and chronic leukaemia, myelomas, lymphomas, myeloproliferative, and lymphoproliferative disorders.
Consultative Haematology Services
Our offerings encompass Allogeneic and Autologous transplants using bone marrow, peripheral blood stem cells, and cord blood stem cells for benign and malignant disorders.
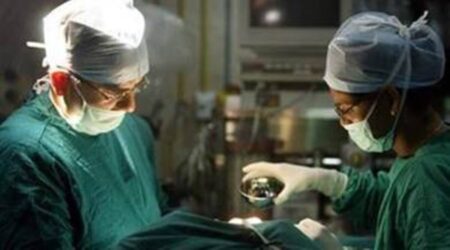
A bone marrow transplant is a therapeutic procedure intended to replace a patient's unhealthy bone marrow with healthy bone marrow cells. This intervention involves the harvesting of bone marrow or peripheral blood stem cells and is commonly employed in the treatment of a variety of blood-related disorders, including leukaemia, lymphoma, and specific autoimmune conditions.
The Vital Role of Bone Marrow
Bone marrow, a soft and spongy substance located within the inner cavities of bones, is essential for blood production. It contains small spaces that house primitive cells with the remarkable ability to mature into different types of blood cells. These unique cells are known as stem cells, and they have the capacity to generate a range of blood cell types, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
Understanding Bone Marrow Types
In general, there are two types of bone marrow: red and yellow. Most children primarily possess red marrow, which is rich in stem cells. However, during adolescence, a significant portion of the bone marrow transforms into yellow marrow due to the infiltration of fat cells. In adolescents, red marrow is typically limited to specific bones, such as the hip bones, breastbone, ribs, shoulder blades, skull, spine, arms, and the ends of the thighs.
- Addressing Malignant Blood Disorders
- Acute Leukaemia (Myeloid & Lymphoid Leukaemia)
- Chronic Leukaemia (Myeloid & Lymphoid Leukaemia)
- Multiple Myeloma
- Myelodysplastic Syndromes
- Hodgkin’s and Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma
- Myeloproliferative Disorders
- Neuroblastoma/Ewing’s Sarcoma, Medulloblastoma
- Treatment for Benign Blood Disorders
- Thalassemia Major & Sickle Cell Disease
- Aplastic Anaemia
- Benign White Blood Cell Disorders - LAD/Congenital Neutropenia
- Immunodeficiency Disorders
- Severe Combined Immunodeficiency Disease
- Congenital and Paediatric Syndromes
- Other Conditions Leading to Bone Marrow Failure – PRCA, PNH, Fanconi's Anaemia
- Adrenoleukodystrophy
- Hemophagocytic Lymph Histiocytosis (HLH) - Both primary and secondary
- Hurler Syndrome
- Multiple Sclerosis/Scleroderma
The utilisation of bone marrow transplant or haematopoietic stem cell transplant is a crucial component in the management of malignant blood disorders, necessitating a combination of chemotherapy and other tailored treatment modalities. These disorders include:
Additionally, bone marrow transplants are used to address non-cancerous, benign blood disorders, offering a comprehensive approach to care. These benign disorders include:
Our bodies rely on a delicate balance between bleeding and clotting. When we're injured, blood clots form to seal the wound and prevent excessive blood loss. However, disorders can disrupt this balance, leading to either excessive bleeding or inappropriate clotting.
Bleeding disorders occur when the blood has difficulty clotting, which can lead to excessive bleeding from even minor injuries or surgeries. Clotting disorders occur when the blood clots too easily and it can increase the risk of developing dangerous blood clots, such as deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE). Some common types of bleeding and clotting disorders includ
Haemophilia:
A genetic disorder that affects a person's ability to produce clotting factors, particularly Factor VIII (haemophilia A) or Factor IX (haemophilia B). Individuals with haemophilia may experience prolonged bleeding, especially after injury or surgery. Joint and muscle bleeding are common complications, which can lead to chronic joint damage if not managed effectively.
Von Willebrand disease:
The most common inherited bleeding disorder, caused by a deficiency in a protein called von Willebrand factor (VWF). Symptoms can vary widely, ranging from mild bruising and nosebleeds to more severe bleeding episodes, particularly in mucous membranes or after surgery or dental procedures.
Platelet disorders:
Such disorders are conditions where platelets, the blood cells responsible for clot formation, do not function properly. This can be due to defects in platelet production, abnormalities in platelet adhesion or aggregation, or medications that interfere with platelet function. Individuals with platelet function disorders may experience easy bruising, mucosal bleeding (such as nosebleeds or gum bleeding), or prolonged bleeding after injury or surgery.
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT):
DVT occurs when a blood clot forms in a deep vein, typically in the legs. It can cause swelling, pain, and redness in the affected limb. If the clot breaks loose and travels to the lungs, it can result in a life-threatening pulmonary embolism.
Pulmonary embolism (PE):
PE occurs when a blood clot, often originating from a DVT in the legs, travels to the lungs and blocks blood flow. Symptoms may include sudden shortness of breath, chest pain, and coughing up blood. PE requires immediate medical attention.
Stroke:
A stroke involves the interruption of blood flow to the brain, either due to a blood clot (ischemic stroke) or bleeding in the brain (haemorrhagic stroke). Clotting disorders, particularly those affecting blood vessels or coagulation factors, can increase the risk of ischemic stroke by causing blood clots to form in the arteries supplying the brain.
Factor V Leiden:
Factor V Leiden is a genetic mutation that predisposes individuals to excessive blood clotting. This mutation affects the function of Factor V, a protein involved in the clotting process, leading to an increased risk of DVT, PE, and other thrombotic events, especially in carriers who are exposed to additional risk factors such as surgery, pregnancy, or oral contraceptive use.
Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS):
This is an autoimmune disorder characterized by the presence of antiphospholipid antibodies, which can increase the risk of blood clots forming in the arteries or veins. APS can lead to recurrent DVT, PE, stroke, and pregnancy complications such as miscarriage or pre-eclampsia.
Thrombophilia:
Thrombophilia refers to a group of conditions characterized by an increased tendency to develop blood clots. This can be due to genetic factors, such as Factor V Leiden mutation or prothrombin gene mutation, or acquired factors, such as antiphospholipid syndrome. Thrombophilia can lead to venous thromboembolism, including deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE).
Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC):
DIC is a complex disorder characterized by widespread activation of the clotting cascade, leading to both excessive clot formation and simultaneous depletion of clotting factors and platelets. It can occur as a complication of various conditions, such as sepsis, trauma, obstetric complications, or certain types of cancer. DIC can result in both bleeding and clotting, leading to multiorgan dysfunction and significant morbidity and mortality if not promptly treated.
Acquired Coagulopathies:
Acquired coagulopathies are conditions where abnormalities in clotting function occur secondary to underlying medical conditions or medications. Examples include liver disease, vitamin K deficiency, certain medications (such as anticoagulants or antiplatelet drugs), and certain types of cancer. Treatment involves addressing the underlying cause and may include supplementation with clotting factors or other medications to manage bleeding or clotting risk.
Diverse Approaches to Bone Marrow Transplant:
The bone marrow transplant process exhibits variability, depending on the donor and transplant procedures. In general, two primary types of transplant processes are recognized:
- Autologous Bone Marrow Transplant:
- Allogeneic Bone Marrow Transplant:
In this method, the patient's own bone marrow or stem cells are harvested and cryopreserved for future use.
This approach involves harvesting bone marrow or stem cells from a donor. The donor could be a relative, often a sibling, or an unrelated person whose bone marrow matches the patient's HLA (Histocompatibility Leukocyte antigen) profile. The transplant of bone marrow occurs on the same day.
Variations in Allogeneic Transplants
Some of the various types of the allogeneic transplants are listed below:
- HLA (Immune)-Match Related Donor (Siblings) Transplant:
- HLA (Immune)-Matched Unrelated Donor Transplant:
- Haplo Identical Donor Transplant:
- Umbilical Cord Blood Transplant:
Typically, the donor is a sibling with a complete HLA match.
The donor is unrelated to the patient but offers a complete HLA match.
Haploidentical donors, often biological parents or half-matched siblings, provide stem cells with a half-matched (haplotype) HLA profile.
Stem cells derived from a newborn's umbilical cord immediately after birth eliminate the need for a perfect match. These stem cells are frozen and preserved for future transplant use.
Transplant Process Overview
After harvesting, the bone marrow or stem cells undergo a filtration process to remove extraneous particles, primarily fat. Subsequently, they are taken to the laboratory for processing, including counting and screening, to prepare them for infusion.
Patient-Centric Approach
The choice between these transplant types depends on the patient's specific medical needs, determined through evaluation by a medical professional. The primary objective of bone marrow transplantation is the management of various blood disorders and specific cancer types.
The Bone Marrow Transplant (BMT) process is divided into three core phases, each with specific functions and considerations. These phases are:
Phase 1: The Pre-BMT Phase
This initial phase encompasses thorough patient assessment and preparation. It involves diagnostic testing, evaluation of the patient's overall health, and the conditioning process to ensure readiness for the transplant.
Phase 2: Stem Cell Transfusion
In this phase, stem cells are transfused into the patient, whether they originate from the patient's own body (autologous) or a donor (allogeneic). This stage represents the actual transplantation of the bone marrow.
Phase 3: The Post-BMT Phase
The post-BMT phase is dedicated to monitoring and facilitating the patient's recovery. It includes the management of potential complications, immune suppression maintenance, and ensuring that the transplanted cells are properly engrafted success of the transplant.
Step 1: Preparation
The patient's journey commences with their arrival at the BMT Centre. Here, the process kicks off with a medical evaluation, the adoption of a multidisciplinary treatment approach, and the insertion of a central venous catheter.
Step 2: Bone Marrow/Stem Cell Harvest
Stem cells are procured either from the bone marrow or peripheral blood through apheresis. In the case of an allogeneic transplant, stem cells are obtained from a donor, whereas in an autologous transplant, they are sourced from the patient.
Step 3: Conditioning
The conditioning phase is the opening step in the transplantation process. It involves the administration of chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or a combination of both. The goal is to impair bone marrow function sufficiently to enhance the chances of curing the disease. Some conditioning treatments may be administered in an outpatient setting, potentially reducing the inpatient stay.
Step 4: Transplant
Immediately following the completion of the conditioning regimen, donor bone marrow or stem cells are infused, akin to a blood transfusion. This marks the onset of the post-BMT phase.
Step 5: Waiting for Engraftment (New Cell Growth)
This stage entails vigilant monitoring and supportive therapy of patients, with a particular focus on preventing infections.
Step 6: Engraftment and Early Recovery
Signs of new bone marrow or stem cell engraftment and development typically become evident around 2 to 3 weeks after transplantation. Monitoring and supportive care persist, while preparations for the patient's discharge commence.
Step 7: Long-Term Recovery
This phase involves the patient's discharge from the centre, discussions on ongoing clinical concerns, and the process of reestablishing their regular lifestyle. Patients are strongly encouraged to schedule routine follow-ups to pre-empt potential long-term complications.
Our centre’s key features include:
- State-of-the-art unit, a one-of-its-kind in the city
- Transplants for infants, children, adults and elderly
- Large spacious transplant suit room with positive pressure ventilation and HEPA filter
- Trained Staff
- Chemotherapy / Immunotherapy / Blood Transfusion
- 24X7 Advanced Critical Care Services
- Daycare facility for outdoor patients
Patients Speak
Hear the heartwarming stories of patients overcoming difficult afflictions












 View Map
View Map Book an Appointment
Book an Appointment Find a Doctor
Find a Doctor Health Check-up
Health Check-up












 Find a Doctor
Find a Doctor Health Checkup
Health Checkup Book an Appointment
Book an Appointment