At Jupiter Hospital, we are equipped with over 30 specialty treatments. There are specialised departments dedicated to illnesses which are backed by skilled and experienced doctors and team of healthcare professionals who are also experts at their craft.
- Bariatric Surgery
- Breast Care Center
- Cardiac Surgery
- Cardiology
- Chest Medicine
- Dental Care
- Dermatology
- ENT
- Endocrinology and Diabetes
- Gastroenterology
- General Surgery and Minimal Access Surgery
- HPB and Surgical Gastroenterology
- Haematology and BMT
- Infectious Diseases
- Internal Medicine
- Interventional Radiology
- Mental Health
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Nutrition and Dietetics
- Obs and Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Organ Transplant
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatrics
- Pain Clinic
- Plastic and Cosmetic Surgery
- Rheumatology
- Robotic Knee Replacement
- Robotic Surgery
- Spine Surgery
- TAVI / TAVR
- Urology
Appointment
Have a query or need to visit an expert? Book an appointment online to consult our doctors and we’ll take care of your needs.
About
Established in 2007, Jupiter Hospital is a tertiary care Hospital with a ‘Patient first’ ideology deeply instilled in its foundation, to deliver leading-edge healthcare to cater to the changing needs of the growing populace.
- Home
- Specialities
- Bariatric Surgery
- Breast Care Center
- Cardiac Surgery
- Cardiology
- Chest Medicine
- Dental Care
- Dermatology
- ENT
- Endocrinology and Diabetes
- Gastroenterology
- General Surgery and Minimal Access Surgery
- HPB and Surgical Gastroenterology
- Haematology and BMT
- Infectious Diseases
- Internal Medicine
- Interventional Radiology
- Mental Health
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Nutrition and Dietetics
- Obs and Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Organ Transplant
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatrics
- Pain Clinic
- Plastic and Cosmetic Surgery
- Rheumatology
- Robotic Knee Replacement
- Robotic Surgery
- Spine Surgery
- TAVI / TAVR
- Urology
- Appointment
- International Patients
- Investor Relations
- About
- Jupiter Foundation
- Careers
- Media Centre
- Contact
- Health Checkup
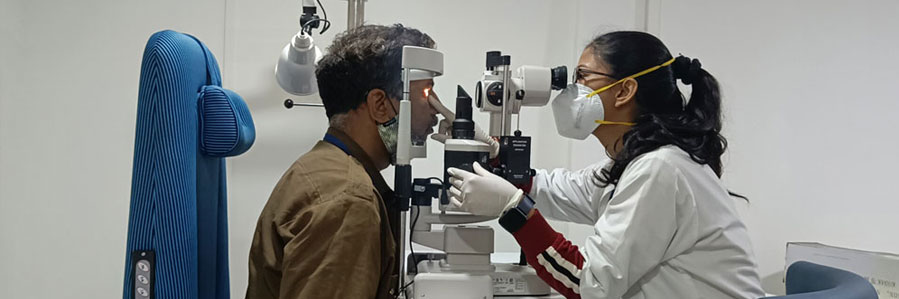
Community Initiatives
Through Jupiter Foundation, we ensure world class health care for the people that are economically challenged. Jupiter Foundation works on the philosophy of putting the patient first in everything.

Careers
At Jupiter, we believe there is a better path to healing that humanizes the practice of health care and inspires hope in the Patient & family who need it most. Our primary value – The needs of the patient come first – is at centre of our plans and decisions. You'll also find that our pride – in where we work, and in what we do – is a common trait. You will be truly part of an amazing team committed to solving the most serious and complex medical challenges.
Media Centre
News & Events
Thane
Eastern Express Highway, Service Rd, Next To Viviana Mall, Thane,
Maharashtra - 400601
Pune
Near Prathamesh Park, Baner, Pimple Nilakh Road,
Pune,
Maharashtra - 411 045
Indore
Scheme No. 94, Sector 1,Ring Road, Near Teen Imli Square,
Indore,
Madhya Pradesh - 452020
Radiation Oncology in Pune
Radiation Oncology: Expert Diagnosis, Treatment Planning, and Ongoing Care
Looking for exceptional Radiation Oncology treatment in Pune? Radiation Oncology involves the use of radiation to eliminate cancer cells. The success of this treatment depends on the precise targeting of the affected area with a maximum dose while minimising damage to surrounding tissues.
Delving into Radiation Oncology
Radiation Oncology, or radiotherapy, is a specialised field of medicine dedicated to combating cancer. It employs high-energy radiation to target and destroy cancer cells within the body. The precision of this treatment is key; it ensures that the radiation focuses on the tumour while safeguarding nearby healthy tissues.
Radiation therapy serves a pivotal role in cancer treatment, and it can be employed at different stages of the disease. Whether as a primary therapy or in conjunction with surgery or chemotherapy, radiation oncology contributes significantly to improving patients' quality of life and long-term outcomes.
Cancer Care with Jupiter Hospital’s Radiation Oncology
Jupiter's Centre for cancer care adopts a comprehensive, multi-disciplinary approach to Radiotherapy treatment. Our Radiation Oncologists collaborates with a team of experts, including Radiation Physicists, Radiation Safety Officers, and Radiotherapists. Our specialists utilise treatment planning technology to treat tumours effectively and reduce the radiation-related side effects at the same time.
Our array of Radiotherapy services at the hospital include the following:
- Conventional Radiotherapy (2D)
- 3DCRT - 3-Dimensional Conformal Radiotherapy
- IMRT - Intensity Modulated Radiotherapy
- IGRT - Image Guided Radiotherapy, with Cardio-respiratory Gating and 6D Couch
- SRT - Stereotactic Radiotherapy
- SBRT - Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy
- SRS - Stereotactic Radiosurgery
Read More
Team

Dr. Chirag Surendra Bhirud
Speciality: Surgical Oncology
Designation: Consultant - Surgical Oncology

Pune

Dr. Jaipalreddy R. Pogal
Speciality: Surgical Oncology
Designation: Consultant - Surgical Oncology

Pune

Dr. Pratik Patil
Speciality: Oncology
Designation: Consultant - Medical Oncology

Pune

Dr. Vikas Kothawade
Speciality: Radiation Oncology
Designation: Consultant - Radiation Oncology

Pune

Dr. Amit Dilip Bhatt
Speciality: Oncology
Designation: Consultant - Medical Oncology

Pune

Dr. Anant Bhushan Ranade
Speciality: Oncology
Designation: Consultant - Medical Oncology

Thane, Pune

Dr. Nikhil Shirsi
Speciality: Oncology
Designation: Consultant - Medical Oncology

Pune

Dr. Sanket Subhash Bankar
Speciality: Surgical Oncology
Designation: Consultant-Surgical Oncology

Pune

Dr. Tushar Patil
Speciality: Oncology
Designation: Consultant - Medical Oncology

Pune
Looking for the Radiation Oncology in Pune
Patients Speak
Hear the heartwarming stories of patients overcoming difficult afflictions











 View Map
View Map Book an Appointment
Book an Appointment Find a Doctor
Find a Doctor Health Check-up
Health Check-up
















































































 Find a Doctor
Find a Doctor Health Checkup
Health Checkup Book an Appointment
Book an Appointment